NFF
The Nature Futures Framework
The Nature Futures Framework (NFF) is a flexible tool designed to support the development of scenarios and models of desirable futures for people, nature and Mother Earth. It responds to the conclusions of the Methodological Assessment Report on Scenarios and Models of the Intergovernmental Science Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), which identified limitations of existing scenario approaches in their usefulness for biodiversity and ecosystem services. The NFF aims to promote the development of nature-centric scenarios that address the plurality of value perspectives on human-nature relationships to inform context- and place-specific policy options.
NFF-based scenario applications could be helpful to illuminate possibilities for achieving the 2050 Vision of ‘Living in harmony with nature’ of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), and support the implementation of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. The Global Biodiversity Framework highlights the importance of considering and bridging different nature values while aiming to enhance nature and people’s relationships with nature. Hence, the NFF is well suited to the implementation of the Global Biodiversity Framework as it is designed to address the multiple nature values.
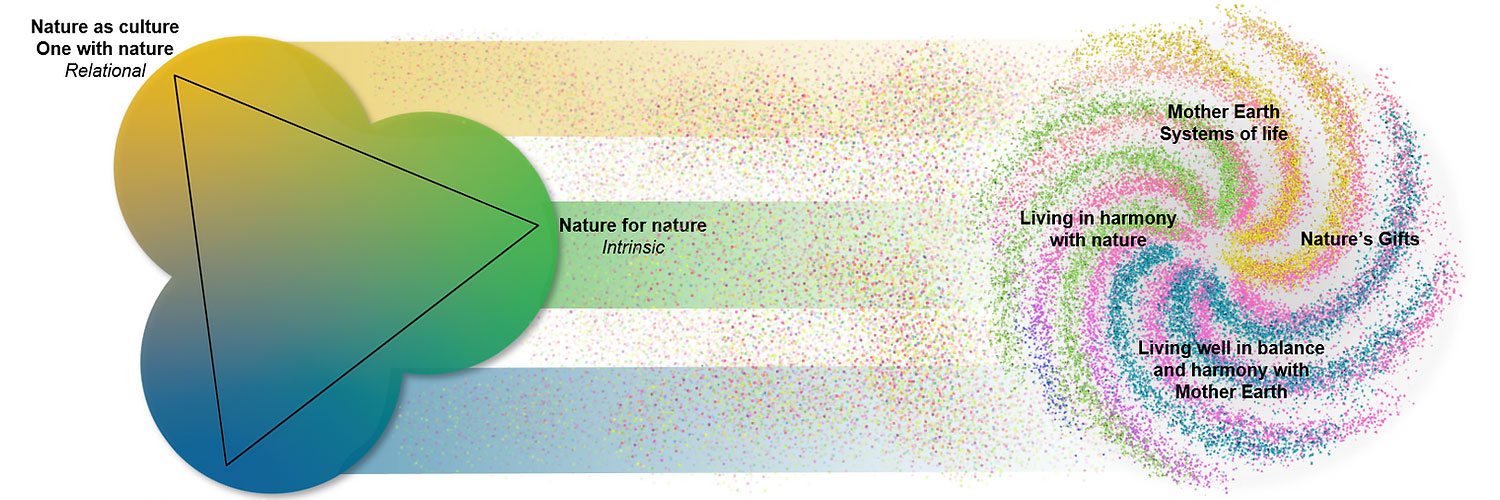
The NFF focuses on three broad value perspectives that people use to relate to nature:
In the nature for nature perspective, people view nature as having intrinsic value, and value is placed on the diversity of species, habitats, ecosystems and processes that form the natural world, and on nature’s ability to function autonomously.
The nature as culture/one with nature perspective primarily highlights relational values of nature, where societies, cultures, traditions and faiths are intertwined with nature in shaping diverse biocultural landscapes.
The nature for society perspective highlights the utilitarian benefits and instrumental values that nature provides to people and societies.
The NFF is represented as a triangle to represent the different mixes of these three value perspectives that different activities can represent. The development of the NFF is explained in Pereira et al (2020).
Below are the scenario case studies in Biosphere Futures that have applied the Nature Futures Framework.
The Nature Futures Framework has been applied in a variety of other ways: at various scales, different places, and diverse purposes. To provide more information on the flexible use of the NFF and to aid its application and development we provide links to this work. We have organised applications of the NFF into six overlapping categories:
Exploration tool
Apply the NFF to a system or problem setting to ‘open up’ for more plural perspectives on nature, and identify diverse values of interest, associated indicators and/or relevant data for monitoring.
For example, Resende et al (2020) used the NFF perspectives to identify different values associated with the water-related ecosystem services in the Brazilian Cerrado.
Classification tool
Use NFF perspectives as a topology for classification and assessment of information.
For example, Diprose et al (2022) used the NFF to make visible the diverse values around nature that are expressed and fostered through the New Zealand Garden Bird Survey.
Translating scenarios
Use the NFF to interpret and translate existing scenarios, for i) classification, assessment and cross-comparison of existing scenarios, or ii) adapting and augmenting existing scenarios into NFF scenarios.
For example, Quintero‐Uribe et al (2022) used the NFF to assess how participatory scenarios for restoring European landscapes depict the future of nature.
Developing visions and scenarios
Use the NFF in the development of visions, pathways and narratives. Fully fledged, integrated NFF scenarios are yet to be developed.
For example, Rana et al (2020) used the NFF to capture the voices of youth in visions of positive futures for nature and people.
Adapting and developing models
Use the NFF to assess model availability, and inspire repurposing or development of new models to quantify part of the NFF space.
For example, Haga et al (2023) modelled desirable futures at local scale by combining the nature futures framework and multi-objective optimization.
Discussing the NFF
Use the NFF to position new work such as concepts, theories or methods, e.g. to explain the relationship with the NFF or to inform its further development.
For example, Greenway (2022) argues that the NFF needs to engage with ‘new materialism thinking’ to help establish harmonious river-human relationships.